Laboratory of Hormonal Regulations in Plants
About us
We are a medium-sized laboratory consisting of seven working groups focused on the auxin transport and homeostasis, metabolism and physiological functions of cytokinins, interaction of plant hormones with the environment, RNA processing, root growth, modelling of phytohormone-mediated cellular processes and advanced analytics of phytohormones.

On both plant tissue culture and whole plant levels we follow the mechanism of action of auxins and cytokinins and their multitude of interactions. The spectrum of methods and approaches we use ranges from molecular biology (gene cloning and tagging, gene editing, transcription profiling, RNAseq), reverse and forward genetics, phenotyping on both cellular and whole plant levels, analytics of phytohormones and their metabolism, to advanced methods of fluorescence confocal microscopy. We always cordially welcome motivated students to work on their bachelor's, master's, and PhD theses, as well as young postdoc researchers from Czechia and abroad.
We organize the international symposium on Auxins and Cytokinins in Plant Development. The last one was held in 2023. We offer a newsletter subscription for those who wish to be informed about the next event, which is expected to take place in 2027.
Group of the auxin transport (Leader: Jan Petrášek)
Our laboratory focuses on the molecular mechanism of polar auxin transport and on the ways of its regulation.
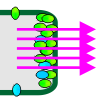 Polar auxin transport (PAT) is the process, in which plant hormone auxin is transported in a cell-to-cell manner. The word “polar” refers to the fact that this type of transport is directional, either within the region of a particular tissue or among tissues. The directionality of PAT is maintained by the interplay of diffusion and carrier-mediated transport of auxin across the plasma membrane. The reason why PAT plays a very important role in plant development is that it helps to establish auxin concentration gradients that subsequently regulate gene expression and also many other post-translational processes.
Polar auxin transport (PAT) is the process, in which plant hormone auxin is transported in a cell-to-cell manner. The word “polar” refers to the fact that this type of transport is directional, either within the region of a particular tissue or among tissues. The directionality of PAT is maintained by the interplay of diffusion and carrier-mediated transport of auxin across the plasma membrane. The reason why PAT plays a very important role in plant development is that it helps to establish auxin concentration gradients that subsequently regulate gene expression and also many other post-translational processes.
Our recent research is focused on the understanding of how plasma membrane-located and endomembrane auxin transporters contribute to the overall auxin homeostasis within the cells. More…
Group of the cytokinin homeostasis regulation (Leader: Klára Hoyerová)
We are engaged in the research of cytokinins – plant hormones that regulate cell division and differentiation.
 Cytokinins are naturally occurring phytohormones that act in concert with auxins to regulate cell division and differentiation and thus efficiently control plant growth and development. Transient enhancement of auxin in relation to cytokinin levels induces root formation while the opposite shift results in shoot formation. The re-establishment of the two hormone quantitative ratios (hormonal homeostasis) is essential for the further development of induced events.
Cytokinins are naturally occurring phytohormones that act in concert with auxins to regulate cell division and differentiation and thus efficiently control plant growth and development. Transient enhancement of auxin in relation to cytokinin levels induces root formation while the opposite shift results in shoot formation. The re-establishment of the two hormone quantitative ratios (hormonal homeostasis) is essential for the further development of induced events.
Our research is focused on the metabolic regulation of intra- and extracellular levels of cytokinins and their cooperation with auxins and other phytohormones to understand cytokinins' physiological role in plants. We are especially interested in the study of pathways and mechanisms down-regulating cytokinin concentrations in plant cells. More…
Group of the role of phytohormones in the interaction with the environment (Leader: Radka Vaňková)
We focus on the elucidation of plant defense mechanisms, with the aim to contribute to the development of effective strategies to enhance the stress tolerance of plants.
 Due to their sessile character, plants had to evolve complex systems of defense against and adaption to variable and often unfavorable environmental conditions. These systems involve mechanisms to sense nutrient abundance or stress conditions and to generate and transduce signals, which result in the modulation of transcription and translation profiles and subsequently of metabolism, leading to effective changes in growth and development. The character of the individual responses depends on the type of stress, its strength, and duration, as well as on the physiological state of the plant, its developmental stage, and the strategy to cope with the particular stress.
Due to their sessile character, plants had to evolve complex systems of defense against and adaption to variable and often unfavorable environmental conditions. These systems involve mechanisms to sense nutrient abundance or stress conditions and to generate and transduce signals, which result in the modulation of transcription and translation profiles and subsequently of metabolism, leading to effective changes in growth and development. The character of the individual responses depends on the type of stress, its strength, and duration, as well as on the physiological state of the plant, its developmental stage, and the strategy to cope with the particular stress.
Our main interest has been the evaluation of hormone functions in abiotic and biotic stress responses, namely their cross-talk, organ specificity and dynamics during stress progression. More…
Group of mathematical modelling (Leader: Petr Hošek)
We use mathematical modelling approach to unravel mechanisms regulating the auxin and cytokinins action in plants.
 Mathematical modelling and similar computational approaches are getting increasingly popular in various fields of biology as they offer the possibility to combine multiple datasets and assay results in order to probe hypotheses or measure properties that cannot be addressed in a single experimental design. We apply mathematical modeling procedures, for example, to describe the transport of plant hormones at the level of isolated cells, to determine the dynamics of metabolic conversions of plant hormones, or to determine the substrate specificity of transport proteins. Down below, we show examples of studies where we employed mathematical modelling methods.
Mathematical modelling and similar computational approaches are getting increasingly popular in various fields of biology as they offer the possibility to combine multiple datasets and assay results in order to probe hypotheses or measure properties that cannot be addressed in a single experimental design. We apply mathematical modeling procedures, for example, to describe the transport of plant hormones at the level of isolated cells, to determine the dynamics of metabolic conversions of plant hormones, or to determine the substrate specificity of transport proteins. Down below, we show examples of studies where we employed mathematical modelling methods.
Group of the MECHANOMICS of directional root growth (Leader: Katarzyna Retzer)
We combine cell biology approaches, advanced imaging methods, and omics data to reveal the molecular mechanisms that support directional root growth.
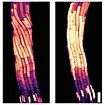 As sessile organisms, plants rely on fine-tuning organ movement to ensure their survival and productivity. Even a subtle loss of directional growth orchestration can have a big impact on plant growth. Roots are three-dimensional objects that grow embedded in soil, and to adjust root movement they regulate the direction of root growth by altering cell expansion continuously to ensure plant survival. Therefore, it is of agricultural importance to study the modulation of cellular expansion in roots upon distinct exogenous stimuli. More...
As sessile organisms, plants rely on fine-tuning organ movement to ensure their survival and productivity. Even a subtle loss of directional growth orchestration can have a big impact on plant growth. Roots are three-dimensional objects that grow embedded in soil, and to adjust root movement they regulate the direction of root growth by altering cell expansion continuously to ensure plant survival. Therefore, it is of agricultural importance to study the modulation of cellular expansion in roots upon distinct exogenous stimuli. More...
Group of the RNA processing in hormonal pathways (Leader: Kamil Růžička)
We aim to use our long-lasting experience with the biology of plant hormones to answer diverse questions relevant to RNA processing.
 RNA processing represents an important, highly intricate, and underexplored layer of gene expression in plants. In contrast, plant hormonal pathways have been relatively well-elucidated. We are a small team that utilizes the excellent lab expertise on hormonal pathways in plants to explore the relevance of key steps of processing of mRNA, particularly alternative splicing (AS) and m6A mRNA methylation. More…
RNA processing represents an important, highly intricate, and underexplored layer of gene expression in plants. In contrast, plant hormonal pathways have been relatively well-elucidated. We are a small team that utilizes the excellent lab expertise on hormonal pathways in plants to explore the relevance of key steps of processing of mRNA, particularly alternative splicing (AS) and m6A mRNA methylation. More…
Analytical unit (Leader: Petr Dobrev)
We improve the existing and develop the new analytical procedures for purification, quantitation and metabolic profiling of plant hormones and other substances of plant origin.
 The progress of the knowledge of hormonal regulation of plant growth and development is dependent on the improvement of existing and the development of new research methods. For this purpose, a separate analytical unit was established in our laboratory, which focuses on the development of modern methods of identification and quantification of plant hormones, as well as monitoring the dynamics of their biosynthesis and metabolic transformations. We can purify and determine the metabolic profile of plant hormones and some other bio-active substances of plant origin. More…
The progress of the knowledge of hormonal regulation of plant growth and development is dependent on the improvement of existing and the development of new research methods. For this purpose, a separate analytical unit was established in our laboratory, which focuses on the development of modern methods of identification and quantification of plant hormones, as well as monitoring the dynamics of their biosynthesis and metabolic transformations. We can purify and determine the metabolic profile of plant hormones and some other bio-active substances of plant origin. More…
Workers
- Ing. Anita Bírošíková
- Mgr. Barbora Svobodová
- Mgr. Julie Talpová
head of the laboratorysenior scientist
- RNDr. Jan Petrášek Ph.D.
deputy head of the laboratoryscientist
- Bc. Ing. Klára Hoyerová PhD.
senior scientist
- Ing. Václav Motyka CSc.
- doc. RNDr. Radomíra Vaňková DSc.
- Prof. RNDr. Eva Zažímalová CSc.
scientist
- Ing. Milada Čovanová PhD.
- Ing. Petre I. Dobrev CSc.
- Ing Jana Jarošová PhD.
- RNDr. Adriana Jelínková PhD.
- Mgr. Petr Klíma Ph.D.
- Ing. Karel Müller PhD.
- Dr. rer. nat. Kamil Růžička
scientific assistant
- RNDr. Martina Laňková PhD.
graduated technical assistant
- Mgr. Nikola Drážná
- Ing. Roberta Filepová
- RNDr. Alena Gaudinová
- Bc. Vojtěch Knirsch
- Eva Kobzová
- ing. Alena Trávníčková
- Mgr. Zuzana Vondrakova
postdoc
- Petr Hošek Ph.D.
- Ing Jozef Lacek
- Ing. Eva Pokorná Ph.D.
- Mgr. Sylva Přerostová Ph.D.
- Dr.nat.techn. Katarzyna Retzer
- Mgr. Roman Skokan
assistant
Research projects
- Physiological, biochemical, molecular and phylogenic characterization of metabolic pathways and mechanisms of cytokinin down-regulation in plants , GA ČR , Václav Motyka
- Anatomical and physiological constraints as key factors governing plant vegetative regeneration from roots , GA ČR , Václav Motyka
- Inactivation of cytokinin-type phytohormones via N- and O-glucosylation – phylogeny and significance in evolution of hormonal homeostatic mechanisms , GA ČR , Václav Motyka
- The role of auxin binding protein 1-mediated signaling in the control of vesicle trafficking in plant cells , GA ČR , Milada Čovanová
- Auxin transport and cytoskeleton in the morphogenesis of plant cells , GA ČR , Jan Petrášek
- Integrating proteomic and genomic tools to contribute evolutionary processes across the plant kingdom with emphasis to the family of cytokinins , GA ČR , Václav Motyka
- Propojení proteomických a genomických přístupů při objasňování evolučních procesů napříč rostlinnou říší s důrazem na rodinu cytokininů , GA ČR , Václav Motyka
- The role of cytokinins and polyamines in heat stress response and thermotolerance in tobacco and Arabidopsis plants , GA ČR , Radomíra Vaňková
- Alternative ways regulating intra- and extracellular concentrations and activities of isoprenoid cytokinins in plants , GA AV , Václav Motyka
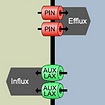
- The role of members of AUX/LAX gene family in auxin influx into plant cell. , GA AV , Klára Hoyerová
Publications
2024
- ENVIRONMENTAL AND EXPERIMENTAL BOTANY 217 105573 2024
- ENVIRONMENTAL AND EXPERIMENTAL BOTANY 105739 2024
- FRONTIERS IN PLANT SCIENCE 14 1296520 2024 Fulltext: PDF link on intranet only
- JOURNAL OF PLANT GROWTH REGULATION 43 727-740 2024 Fulltext: PDF link on intranet only
- NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 15 2024 (External fulltext)
- PLANT CELL 2024 Fulltext: public PDF link
- SCIENCE OF THE TOTAL ENVIRONMENT 914 169914 2024
2023
- PLANT JOURNAL 115 470-479 2023 (External fulltext)
- PLANT PHYSIOLOGY AND BIOCHEMISTRY 198 107683 2023
- Plant Hormones and Climate Change 2023
